Upcycling
Fall Upcycled baking
This fall at NETZRO, we’re celebrating apple season by baking all of the upcycled goodies we can with the best local apples we can find. We mean no disrespect to the ever-popular pumpkin spice but, surrounded by a seemingly infinite array of Minnesotan apples, it feels like it would be a real shame not to…
COVID19, Finding a new path forward
The past few months have been a time of unprecedented uncertainty for us at NETZRO and for the world. We have all faced hardships and seen drastic changes to the way the world around us operates, from business to social interaction to the underlying fear and anxiety in our everyday lives. Living and working in…
REHARVEST – NETZRO’s third “R” of Upcycling
Reuse, Restore, New uses, Innovation, Functional Health With reducing and recovering squared away, we arrive at the third and final R of food upcycling: “reharvest.” Reharvesting focuses on taking recovered food byproducts and increasing their value by integrating them into new food products. Examples of this include taking discarded parts of fruit and processing them…
RECOVER – NETZRO’s Second “R” Of Upcycling
As we covered in the first article of this series, food upcycling is one important way to reduce food waste by making the most of food byproducts that are underutilized because they have traditionally been seen as waste. How do we accomplish this? This brings us to our second R of food upcycling: recover. …
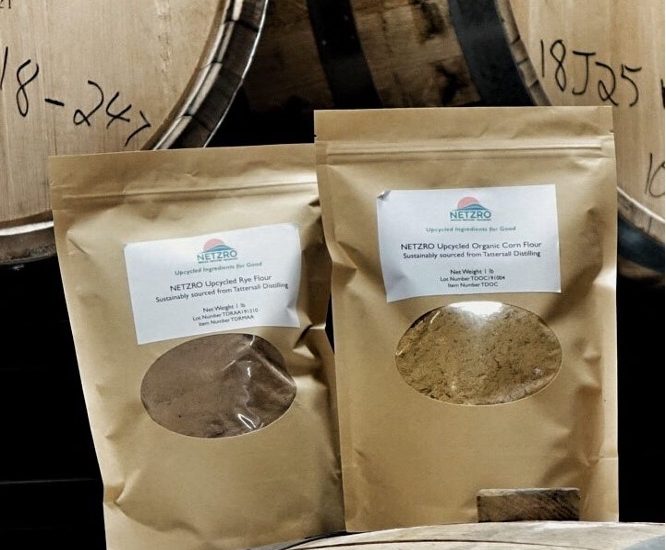
REDUCE – NETZRO’s First ‘R” of Upcycling
Roughly one third of food produced in the world for human consumption gets lost or wasted. National Geographic is projecting more than 9 billion mouths to feed by 2050, requiring food producers to double the amount of food currently in production. ReFED was formed to build a different future, where food waste prevention is recognized…
My Semester of Food Upcycling
Since January, I have served as NetZro’s Digital Communications and Brewers’ Spent Grain (BSG) Recipe Development Intern. Throughout this process, I have worked to incorporate more sustainable food practices into my own life. Today I’ll be sharing my experience working for NetZro and trying to become a more sustainable consumer, baker, and overall human being!…
Trash to Treasure
Upcycling Explained When a product is recycled, it is processed for reuse but most often in a way that downgrades its quality, giving it a new use but as a product of lesser value. Upcycling solves this problem by reusing products in ways that uphold or improve their quality. For example, recycling could look like…
- « Previous
- 1
- 2